Grating Couplers
Grating couplers
Source Code
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
# Import necessary packages
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import gdsfactory as gf
import meep as mp
import gplugins.gmeep as gm
import gdsfactory.cross_section as xs
import gplugins.modes as gmode
import gplugins.gmeep as gmeep
import pandas as pd
1
2
Using MPI version 4.1, 1 processes
[32m2025-10-24 18:01:50.627[0m | [1mINFO [0m | [36mgplugins.gmeep[0m:[36m<module>[0m:[36m39[0m - [1mMeep '1.31.0' installed at ['/home/ramprakash/anaconda3/envs/si_photo/lib/python3.13/site-packages/meep'][0m
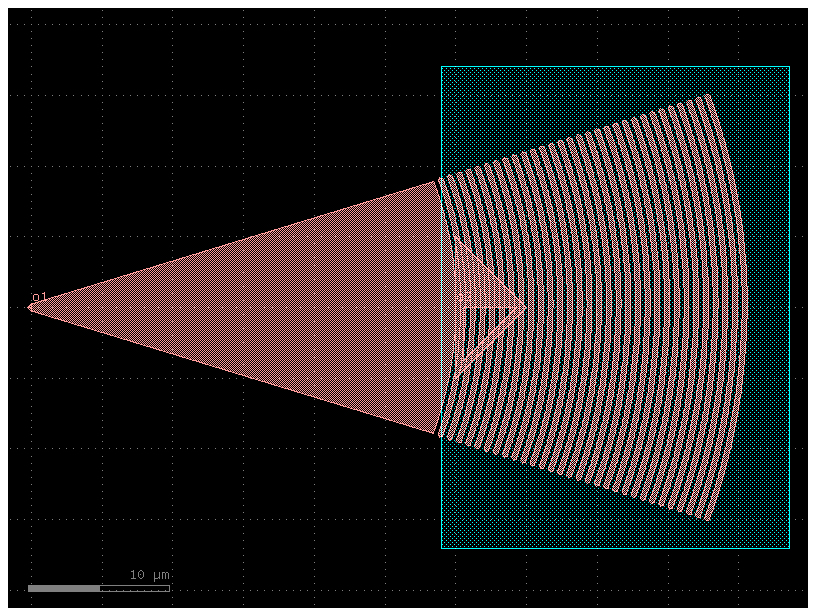
Rectangular grating coupler from GDSFactory
Source Code
1
2
3
4
gf.clear_cache
rect_gc = gf.components.grating_coupler_rectangular(n_periods=20, period=0.75, fill_factor=0.5, width_grating=11.0, length_taper=10.0, polarization='te', wavelength=1.55, taper='taper', layer_slab='SLAB150', layer_grating=None, fiber_angle=15, slab_xmin=-1.0, slab_offset=1.0, cross_section='strip')
# rect_gc.draw_ports()
rect_gc.plot()
Source Code
1
2
scene = rect_gc.to_3d()
scene.show()
Using Gplugins gmeep for the uniform 2D grating coupling simulations
The effective the effective index of the 220 nm slab is about neff1 = 2.848, and the effective index of the shallow etched region with thickness 150 nm is about neff2 =2.534, at λ0 = 1550 nm. For the Fill fraction of 50%.
The weighted-average index of the grating region, neffm is then
$n_{eff} = FF.n_{eff1}+(1-ff).n_{eff2}$
$n_{eff} = 2.691$
From, the Bragg condition and for the incident angle in air is 20 deg
$\Lambda = \frac{\lambda}{n_{eff}-sin\theta_{air}}$
$\Lambda = 660 nm $ Period of the grating
Source Code
1
help(gmeep.write_sparameters_grating)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
Help on function write_sparameters_grating in module gplugins.gmeep.write_sparameters_grating:
write_sparameters_grating(
plot: 'bool' = False,
plot_contour: 'bool' = False,
animate: 'bool' = False,
overwrite: 'bool' = False,
dirpath: 'PathType | None' = PosixPath('/home/ramprakash/.gdsfactory/sp'),
decay_by: 'float' = 0.001,
verbosity: 'int' = 0,
**settings
) -> 'dict[str, np.ndarray]'
Write grating coupler with fiber Sparameters.
Args:
plot: plot simulation (do not run).
plot_contour: show contours.
animate: create animation.
overwrite: overwrites simulation if found.
dirpath: directory path.
decay_by: field decay to stop simulation.
verbosity: print messages.
core_materials: number of cores.
Keyword Args:
period: fiber grating period in um.
fill_factor: fraction of the grating period filled with the grating material.
n_periods: number of periods.
widths: Optional list of widths. Overrides period, fill_factor, n_periods.
gaps: Optional list of gaps. Overrides period, fill_factor, n_periods.
fiber_angle_deg: fiber angle in degrees.
fiber_xposition: xposition.
fiber_core_diameter: fiber diameter.
fiber_numerical_aperture: NA.
fiber_clad_material: fiber cladding index.
nwg: waveguide index.
nslab: slab refractive index.
clad_material: top cladding index.
nbox: box index bottom.
nsubstrate: index substrate.
pml_thickness: pml_thickness (um).
substrate_thickness: substrate_thickness (um).
box_thickness: thickness for bottom cladding (um).
core_thickness: core_thickness (um).
slab_thickness: slab thickness (um). etch_depth=core_thickness-slab_thickness.
top_clad_thickness: thickness of the top cladding.
air_gap_thickness: air gap thickness.
fiber_thickness: fiber_thickness.
resolution: resolution pixels/um.
wavelength_start: min wavelength (um).
wavelength_stop: max wavelength (um).
wavelength_points: wavelength points.
eps_averaging: epsilon averaging.
fiber_port_y_offset_from_air: y_offset from fiber to air (um).
waveguide_port_x_offset_from_grating_start: in um.
fiber_port_x_size: in um.
xmargin: margin from PML to grating end in um.
.. code::
fiber_xposition
|
fiber_core_diameter
/ / / / |
/ / / / | fiber_thickness
/ / / / _ _ _| _ _ _ _ _ _ _
|
| air_gap_thickness
_ _ _| _ _ _ _ _ _ _
|
clad_material | top_clad_thickness
_ _ _| _ _ _ _ _ _ _
_|-|_|-|_|-|___ | _| etch_depth
core_material | |core_thickness
______________|_ _ _|_ _ _ _ _ _ _ _
|
nbox |box_thickness
______________ _ _ _|_ _ _ _ _ _ _ _
|
nsubstrate |substrate_thickness
______________ _ _ _|
Source Code
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
fiber_angle_deg = 20
period = 0.66
ff = 0.5
nSi = 3.45
nSiO2 = 1.45
fiber_y_offset_air = 3
fiber_x_pos = 1
core_thickness = 0.220
slab_thickness = 0.150
waveguide_port_x_offset = 10
n_periods = 30
start_wvl = 1.45
end_wvl = 1.65
gmeep.write_sparameters_grating(
plot=True,
plot_contour=True,
fiber_angle_deg=fiber_angle_deg,
period=period,
fill_factor=ff,
nwg=nSi,
nslab=nSi,
nbox=nSiO2,
clad_material=nSiO2,
nsubstrate=nSi,
wavelength_start=start_wvl,
wavelength_stop=end_wvl,
fiber_xposition=fiber_x_pos,
waveguide_port_x_offset_from_grating_start=waveguide_port_x_offset,
n_periods=n_periods
)
1
Warning: grid volume is not an integer number of pixels; cell size will be rounded to nearest pixel.
Source Code
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
# Run simulation
sp2 = gmeep.write_sparameters_grating(
plot=False,
plot_contour=False,
fiber_angle_deg=fiber_angle_deg,
period=period,
fill_factor=ff,
nwg=nSi,
nslab=nSi,
nbox=nSiO2,
clad_material=nSiO2,
nsubstrate=nSi,
fiber_xposition=fiber_x_pos,
waveguide_port_x_offset_from_grating_start=waveguide_port_x_offset,
n_periods=n_periods,
wavelength_start=start_wvl,
wavelength_stop=end_wvl,
animate=True,
dirpath = '/home/ramprakash/Integrated_Tests/GC_temp',
resolution=20
)
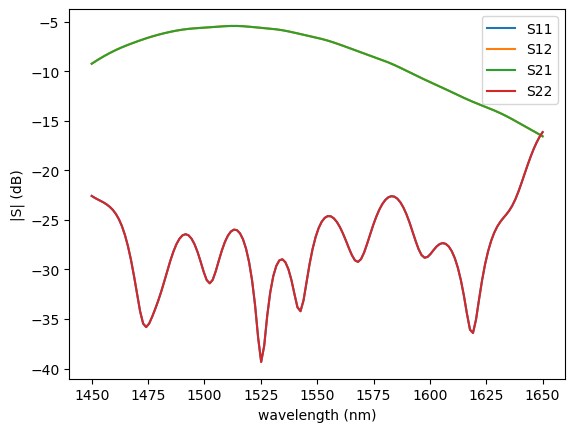
Maximum transmission is shifted from 1550 nm. Optimization of other parameters and higher resolution will give the desired trasnmission.
Source Code
1
gmeep.plot.plot_sparameters(sp2)
Futher studies can be done by varying the location of the fiber, changing the periods, fill fraction etc…
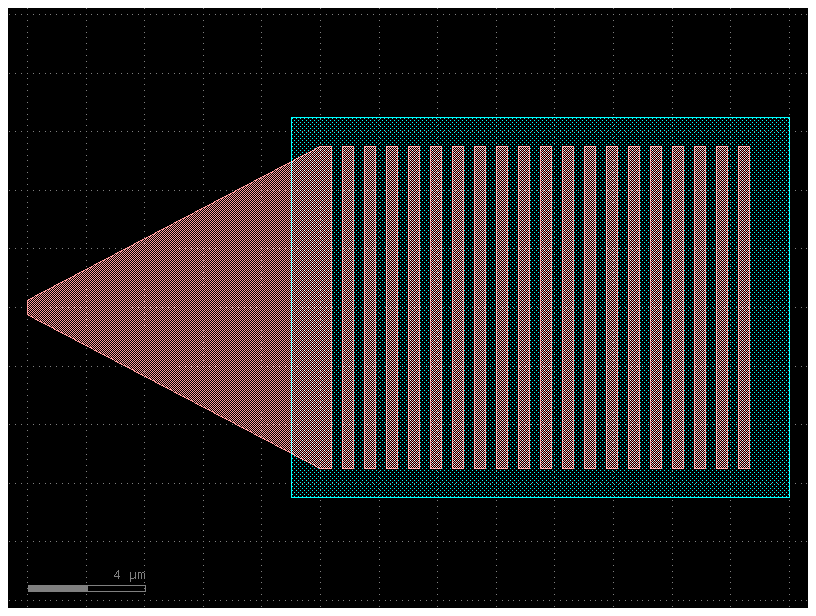
Focusing coupler
To make compact coupler without tapper.
Source Code
1
2
3
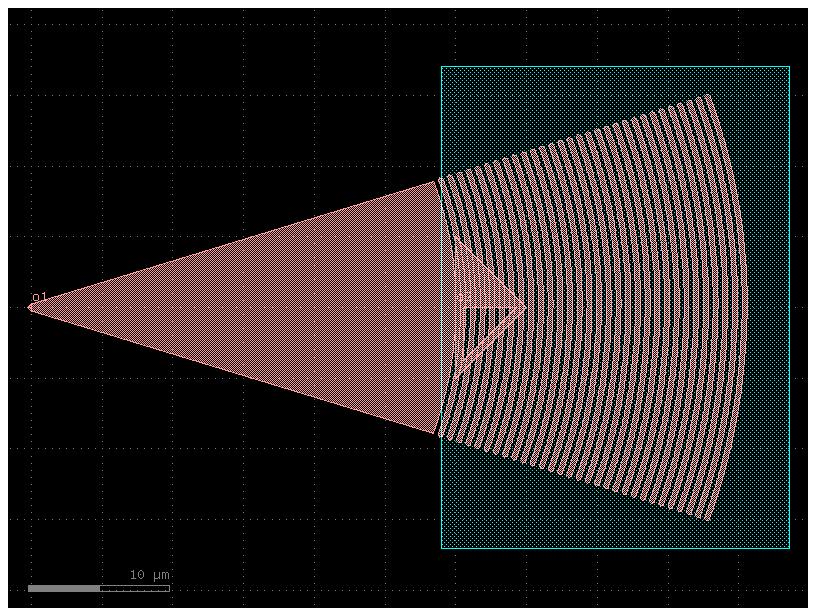
focus_coupler = gf.components.grating_coupler_elliptical(polarization='te', taper_length=30, taper_angle=40, wavelength=1.554, fiber_angle=15, grating_line_width=0.343, neff=2.638, nclad=1.443, n_periods=30, big_last_tooth=False, layer_slab='SLAB150', slab_xmin=-1, slab_offset=2, spiked=True, cross_section='strip').copy()
focus_coupler.draw_ports()
focus_coupler.plot()
Source Code
1
2
scene = focus_coupler.to_3d()
scene.show()
Modeling with MEEP
Trying 3D simulations from the GDSfactory component
Source Code
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
194
195
196
197
198
199
200
201
202
203
204
205
206
207
208
209
210
211
212
213
214
215
216
217
218
219
220
221
222
223
224
225
226
227
228
229
230
231
232
233
234
235
236
%%writefile fgc_MPI_sim.py
import gplugins.modes as gmode
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import meep as mp
import gdsfactory as gf
import gplugins.gmeep as gm
import gdsfactory.cross_section as xs
import sys
mp.verbosity(3)
sys.stdout.flush()
# Set up frequency points for simulation
npoints = 50
lcen = 1.492
dlam = 0.100
wl = np.linspace(lcen - dlam / 2, lcen + dlam / 2, npoints)
fcen = 1 / lcen
fwidth = 3 * dlam / lcen**2
fpoints = 1 / wl
# Center frequency mode_parity
mode_parity = mp.ODD_Y #mp.EVEN_Y + mp.ODD_Z
dpml = 2
dpad = 2
resolution = 10
# Define materials
Si = mp.Medium(index=3.45)
SiO2 = mp.Medium(index=1.45)
focus_coupler = gf.components.grating_coupler_elliptical(polarization='tm', taper_length=16.6, taper_angle=40, wavelength=1.554, fiber_angle=15, grating_line_width=0.343, neff=2.638, nclad=1.45, n_periods=30, big_last_tooth=False, layer_slab='SLAB150', slab_xmin=-1, slab_offset=2, spiked=True, cross_section='strip').copy()
sub_t = 2
sio_t = 2
si_t = 0.220
air_t = 1
cladding_t = 1
sx = focus_coupler.xsize + 2 * dpml + 2
sy = focus_coupler.ysize + 2 * dpml + 2 * dpad
sz = 2*(sub_t+sio_t+si_t+dpml+air_t)
# Cell size
cell_size = mp.Vector3(sx,sy,sz)
# Create the ring resonator component
focus_coupler = gf.components.extend_ports(focus_coupler, port_names=["o1"], length=6)
focus_coupler = focus_coupler.copy()
focus_coupler.flatten()
focus_coupler.center = (0, 0)
# Get geometry from component
coupler_geo = gm.get_meep_geometry.get_meep_geometry_from_component(focus_coupler, is_3d=True)
geometry = []
# SiO2 cladding
geometry.append(
mp.Block(
center=mp.Vector3(0, 0, si_t/2),
size=(mp.inf, mp.inf, cladding_t),
material=SiO2
)
)
# GC geometry
geometry += [
mp.Prism(geom.vertices, geom.height, geom.axis, geom.center, material=Si)
for geom in coupler_geo
]
# geometry.append(geom_coupler)
# SiO2 slab
geometry.append(
mp.Block(center=mp.Vector3(0, 0, -sio_t/2), size=(mp.inf, mp.inf, sio_t), material=SiO2)
)
# Si substrate
geometry.append(
mp.Block(center=mp.Vector3(0, 0, -sio_t-sub_t/2), size=(mp.inf, mp.inf, sub_t), material=Si)
)
src = mp.GaussianSource(frequency=fcen, fwidth=fwidth)
source = [
mp.EigenModeSource(
src=src,
eig_band=1,
eig_parity=mode_parity,
eig_kpoint=mp.Vector3(1,0,0),
direction=mp.NO_DIRECTION,
size=mp.Vector3(0,1,si_t+sio_t),
center=mp.Vector3(focus_coupler.ports["o1"].x+dpml+2, focus_coupler.ports["o1"].y, 0),
amplitude=1
),
]
symmetries = [mp.Mirror(mp.Y,-1)]
sim = mp.Simulation(
resolution=resolution,
cell_size=cell_size,
boundary_layers=[mp.Absorber(dpml)],
sources=source,
geometry=geometry,
dimensions=3,
symmetries=symmetries
)
waveguide_monitor_port = mp.ModeRegion(
size=mp.Vector3(0,1,si_t+sio_t),
center=mp.Vector3(focus_coupler.ports["o1"].x+dpml+2+1, focus_coupler.ports["o1"].y, 0),
)
waveguide_monitor = sim.add_mode_monitor(fpoints, waveguide_monitor_port)
fiber_monitor_port = mp.ModeRegion(
size=mp.Vector3(focus_coupler.xsize/2,focus_coupler.ysize,0),
center=mp.Vector3(30*0.3,0,sio_t+air_t)
)
fiber_monitor = sim.add_mode_monitor(fpoints, fiber_monitor_port)
whole_dft = sim.add_dft_fields([mp.Ey], fcen, 0, 1, center=mp.Vector3(0,0,0), size=mp.Vector3(sx,0,sz))
whole_dft_2 = sim.add_dft_fields([mp.Ey], fcen, 0, 1, center=mp.Vector3(0, 0, 0.160), size=mp.Vector3(sx, sy,0),)
vol1 = mp.Volume(
center=mp.Vector3(0, 0, 0),
size=mp.Vector3(sx, 0,sz)
)
vol2 = mp.Volume(
center=mp.Vector3(0, 0, 0.160),
size=mp.Vector3(sx, sy,0),)
if mp.am_master():
eps_parameters = dict(contour=True)
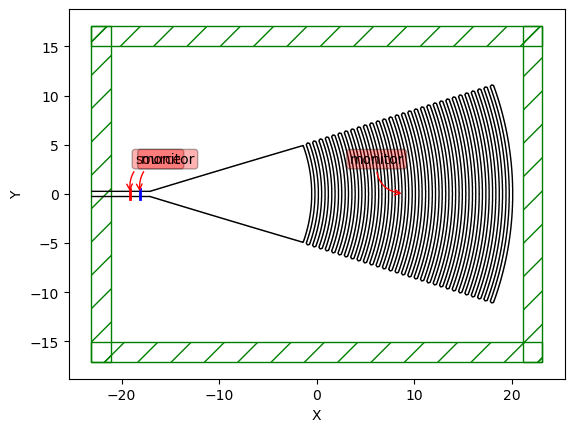
sim.plot2D(output_plane=vol1, eps_parameters=eps_parameters,labels=True)
plt.savefig('Grating_coupler_sim.png', dpi=150, bbox_inches='tight')
plt.close()
eps_parameters = dict(contour=True)
sim.plot2D(output_plane=vol2, eps_parameters=eps_parameters,labels=True)
plt.savefig('Grating_coupler_sim_2.png', dpi=150, bbox_inches='tight')
plt.close()
def progress(sim):
if mp.am_master():
print(f"t = {sim.meep_time():.1f}")
sys.stdout.flush()
sim.run(mp.at_every(10, progress),
until_after_sources=mp.stop_when_energy_decayed(dt=50, decay_by=1e-4))
# mp.stop_when_fields_decayed(
# 20, mp.Ey, mp.Vector3(focus_coupler.ports["o1"].x+dpml+2,0,0), 1e-6))
# waveguide_mode = sim.get_eigenmode_coefficients(
# waveguide_monitor,
# [1],
# eig_parity=mode_parity,
# direction=mp.X,
# eig_tolerance=5E-5,)
# fiber_angle_deg = 15
# n_eff = 1.45
# fiber_mode = sim.get_eigenmode_coefficients(
# fiber_monitor,
# [1],
# direction=mp.NO_DIRECTION,
# eig_parity=mode_parity,
# eig_tolerance=5E-5,
# kpoint_func = lambda f, n: mp.Vector3(
# 2 * np.pi * f * n_eff * np.sin(np.radians(fiber_angle_deg)),
# 0,
# 2 * np.pi * f * n_eff * np.cos(np.radians(fiber_angle_deg))
# ), # Hardcoded index for now, pull from simulation eventually
# )
# a1 = waveguide_mode.alpha[:, :, 0].flatten()
# b1 = waveguide_mode.alpha[:, :, 1].flatten()
# a2 = fiber_mode.alpha[:, :, 0].flatten()
# eps_data = sim.get_epsilon(center=mp.Vector3(0,0,0), size=mp.Vector3(sx,0,sz))
ez_data = sim.get_dft_array(whole_dft,mp.Ey,0)
# eps_data_2 = sim.get_epsilon(center=mp.Vector3(0, 0, 0.160), size=mp.Vector3(sx, sy,0))
ez_data_2 = sim.get_dft_array(whole_dft_2,mp.Ey,0)
# s11 = np.squeeze(b1 / a1)
# s12 = np.squeeze(a2 / a1)
# s21 = s12
# s22 = s11
# Save results (only from master process)
if mp.am_master():
# np.save('fgc_wavelengths.npy', wl)
# np.save('fgc_s11.npy', s11)
# np.save('fgc_s12.npy', s12)
# np.save('fgc_eps_data.npy', eps_data)
np.save('fgc_ez_data.npy', ez_data)
# np.save('fgc_eps_data_2.npy', eps_data_2)
np.save('fgc_ez_data_2.npy', ez_data_2)
# Create field plot
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(12, 8))
ax_field = fig.add_subplot(1, 1, 1)
ax_field.set_title("Steady State Fields")
# ax_field.imshow(
# np.flipud(np.transpose(eps_data)),
# interpolation="spline36",
# cmap="binary"
# )
ax_field.imshow(
np.flipud(np.transpose(np.real(ez_data))),
interpolation="spline36",
cmap="RdBu",
alpha=0.9,
)
ax_field.axis("off")
plt.savefig('fgc_steady_state_fields.png', dpi=150, bbox_inches='tight')
plt.close()
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(12, 8))
ax_field = fig.add_subplot(1, 1, 1)
ax_field.set_title("Steady State Fields")
# ax_field.imshow(
# np.flipud(np.transpose(eps_data)),
# interpolation="spline36",
# cmap="binary"
# )
ax_field.imshow(
np.flipud(np.transpose(np.real(ez_data_2))),
interpolation="spline36",
cmap="RdBu",
alpha=0.9,
)
ax_field.axis("off")
plt.savefig('fgc_steady_state_fields_2.png', dpi=150, bbox_inches='tight')
plt.close()
print("Simulation completed successfully!")
print(f"Results saved to: wavelengths.npy, port1_coeff.npy, port2_coeff.npy, eps_data.npy, ez_data.npy")
print(f"Plots saved to: simulation_geometry.png, steady_state_fields.png")
1
Overwriting fgc_MPI_sim.py
Source Code
1
2
3
4
5
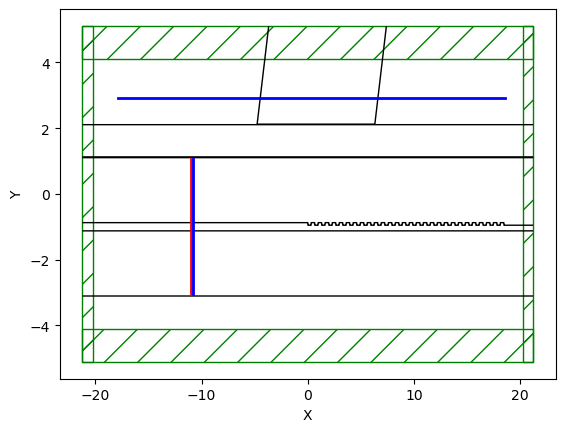
vol1 = mp.Volume(
center=mp.Vector3(0, 0, 0.160),
size=mp.Vector3(sx, sy,0),)
eps_parameters = dict(contour=True)
sim.plot2D(output_plane=vol1, eps_parameters=eps_parameters,labels=True)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
Warning: grid volume is not an integer number of pixels; cell size will be rounded to nearest pixel.
<Axes: xlabel='X', ylabel='Y'>
Source Code
1
!mpirun -np 34 python fgc_MPI_sim.py
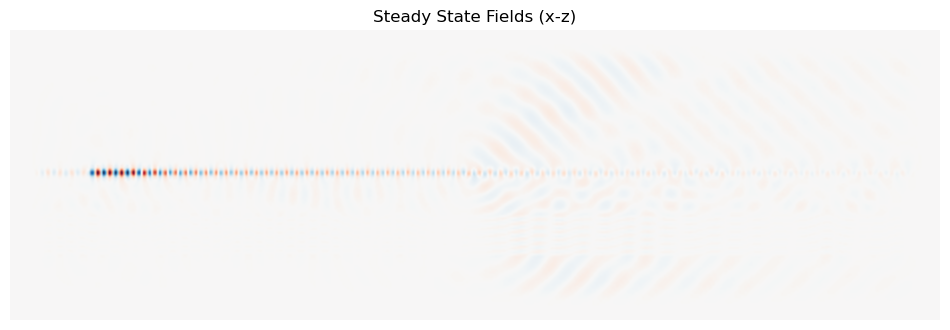
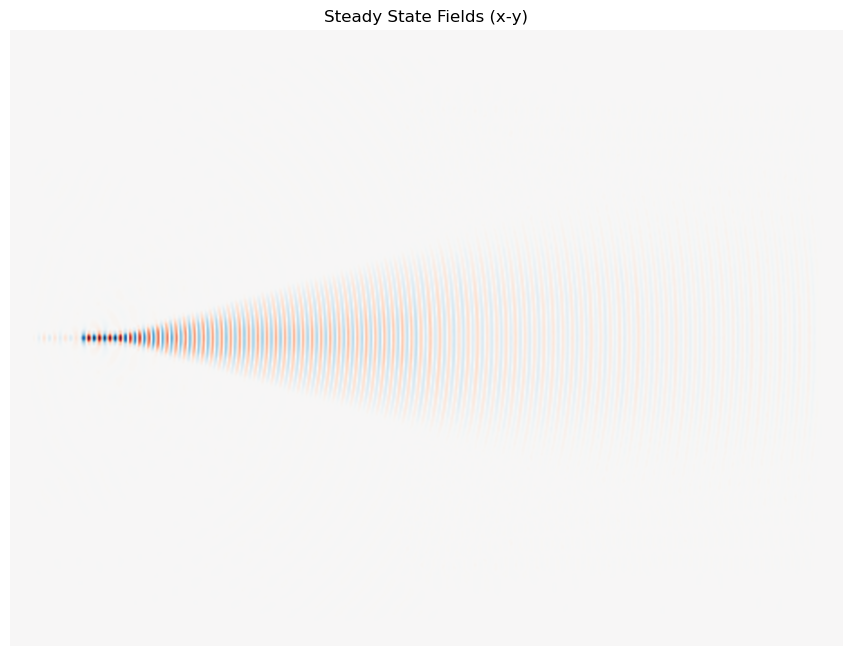
Due to computational cost for mode decompostion only the steady state fields are calculated.
Source Code
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# Load results
# wl = np.load('fgc_wavelengths.npy')
# port1_coeff = np.load('fgc_s11.npy')
# port2_coeff = np.load('fgc_s12.npy')
# port3_coeff = np.load('RingDob_port3_coeff.npy')
# port4_coeff = np.load('RingDob_port4_coeff.npy')
# eps_data = np.load('RingDob_eps_data.npy')
ez_data = np.load('fgc_ez_data.npy')
ez_data_2 = np.load('fgc_ez_data_2.npy')
# # Plot transmission spectrum
# fig, (ax1, ax2, ax3, ax4) = plt.subplots(4, 1, figsize=(10, 8))
# # S11 (reflection)
# ax1.plot(wl, 10*np.log10(np.abs(port1_coeff)**2), 'b-', linewidth=2)
# ax1.set_ylabel('Reflectance |S11|²')
# ax1.set_title('Port 1 Reflection')
# ax1.grid(True, alpha=0.3)
# # S21 (transmission)
# ax2.plot(wl, 10*np.log10(np.abs(port2_coeff)**2), 'r-', linewidth=2)
# ax2.set_xlabel('Wavelength (μm)')
# ax2.set_ylabel('Transmittance |S21|²')
# ax2.set_title('Port 2 Transmission')
# ax2.grid(True, alpha=0.3)
# # S31 (transmission)
# ax3.plot(wl, 10*np.log10(np.abs(port3_coeff)**2), 'r-', linewidth=2)
# ax3.set_xlabel('Wavelength (μm)')
# ax3.set_ylabel('Transmittance |S31|²')
# ax3.set_title('Port 3 Transmission')
# ax3.grid(True, alpha=0.3)
# # S41 (transmission)
# ax4.plot(wl, 10*np.log10(np.abs(port4_coeff)**2), 'r-', linewidth=2)
# ax4.set_xlabel('Wavelength (μm)')
# ax4.set_ylabel('Transmittance |S41|²')
# ax4.set_title('Port 4 Transmission')
# ax4.grid(True, alpha=0.3)
# plt.tight_layout()
# plt.savefig('transmission_spectrum.png', dpi=150, bbox_inches='tight')
# plt.show()
# print(f"Peak transmission: {np.min(np.abs(port2_coeff)**2):.4f}")
# print(f"Resonance wavelength: {wl[np.argmin(np.abs(port2_coeff)**2)]:.4f} μm")
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(12, 8))
ax_field = fig.add_subplot(1, 1, 1)
ax_field.set_title("Steady State Fields (x-z)")
# ax_field.imshow(
# np.flipud(np.transpose(eps_data)),
# interpolation="spline36",
# cmap="binary")
ax_field.imshow(
np.flipud(np.transpose(np.real(ez_data))),
interpolation="spline36",
cmap="RdBu",
alpha=0.9,
)
ax_field.axis("off")
plt.show()
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(12, 8))
ax_field = fig.add_subplot(1, 1, 1)
ax_field.set_title("Steady State Fields (x-y)")
# ax_field.imshow(
# np.flipud(np.transpose(eps_data)),
# interpolation="spline36",
# cmap="binary")
ax_field.imshow(
np.flipud(np.transpose(np.real(ez_data_2))),
interpolation="spline36",
cmap="RdBu",
alpha=0.9,
)
ax_field.axis("off")
plt.show()
TODO: More simualtion for the far-field coupling angle and optmization